异常是导致程序中断运行的一种指令流,如果不对异常进行正确处理,则可能导致程序的中断运行,造成不必要的损失。
当程序的运行出现逻辑错误,或出现无效的情况时,即为发生了异常。
- Java 定义的异常全部基于
Throwable,基本继承于 Throwable 的两个子类Error和Exception - 其中 Error 仅发生在 JVM 级别的错误时才会抛出,一般程序不会处理。
类图如下:
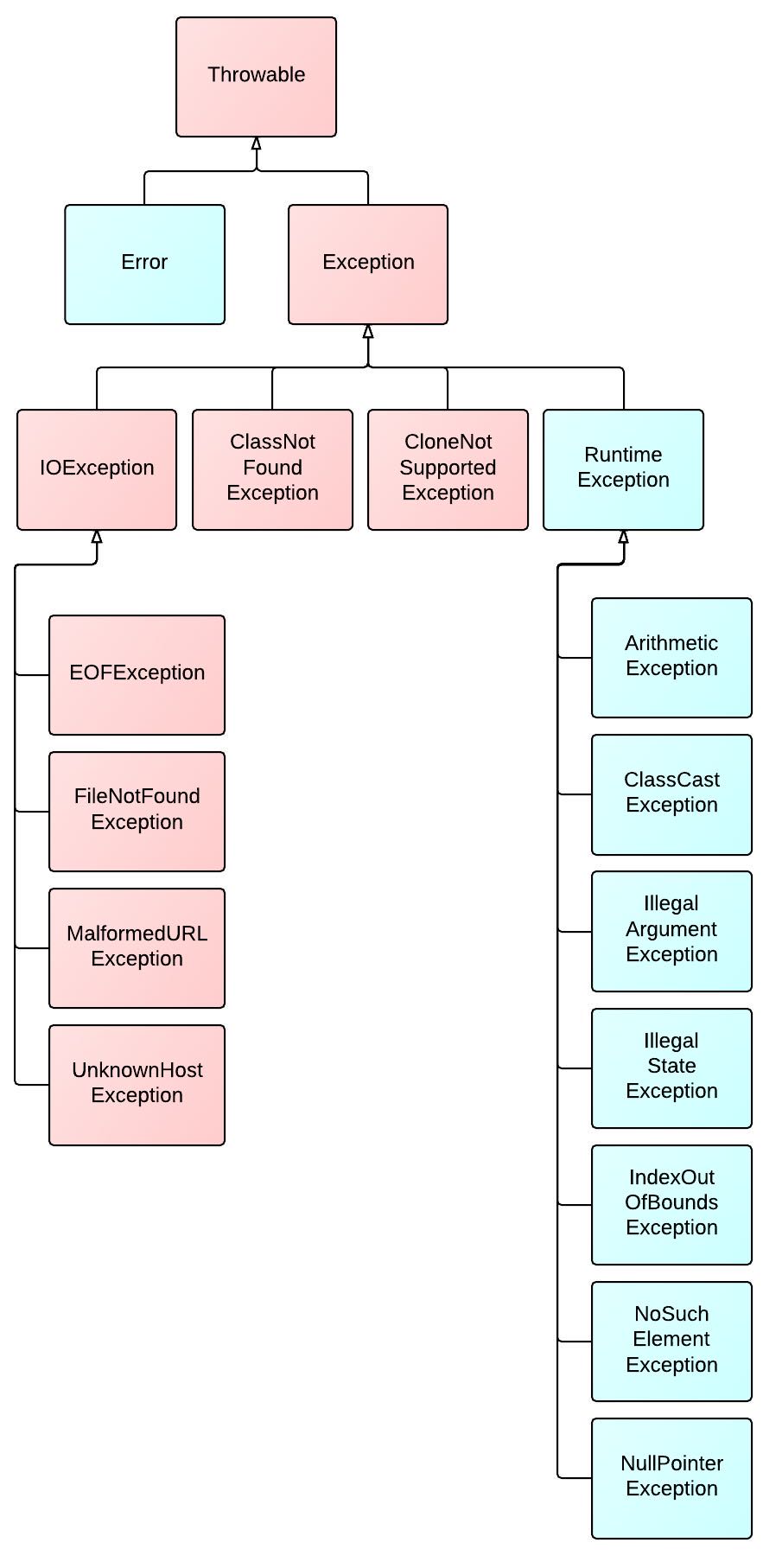
Unchecked Exception
运行时异常
- 表示错误,即程序的问题或逻辑错误,运行的时候无法恢复,不需要抛出异常
- 包括
Error,RuntimeException及其子类,如:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9OutOfMemoryError
IllegalArgumentException
NullPointerException
IllegalStatementException
ClassCastException
ClassNotFoundException
IndexOutOfBoundException
NoSuchMethodException
ArithmeticException - Error:系统级的错误和程序不必处理的异常
Checked Exception
受检查异常(非运行时异常)
- 表示无效操作,即不是程序可以预测的异常,比如无效的用户输入、文件不存在等
- 必须显式地捕获处理(try / catch)或向外抛出(throws)
- 上图红色类即为非运行时异常
- 包括 Exception 除 RuntimeException 之外的所有子类,如:
1
2
3
4FileNotFoundException
SocketException
SQLException
IOException - extends Exception
处理异常
通常我们要处理 Checked Exception,可以使用 throws 关键字或 try-catch 块进行处理。
throws
- 如果要监控整个方法中的某一类异常,且将其往外抛出,可使用
throws关键字 - 当方法 return 前,任何一句代码发生对应异常,或使用
throw关键字手动抛出的时候,异常都会向外抛出,交由外层调用方法进行处理
1 | public void divide(int a, int b) throws Exception { |
throw 和 throws 比较
- throws 出现在方法函数头,throw 出现在函数体;
- throws 表示出现异常的一种可能性,声明可能会抛出一个异常,并不一定发生该种异常;
- throw 则是真实抛出了异常:执行 throw 则一定抛出了某种异常
try-catch-finally
- 如需要对某一块代码中的代码进行监控,且有意对异常在方法内进行处理:使用 try-catch 块
- 在 try-catch 块中仍可配合 throw/throws 将异常外抛
基本格式1
2
3
4
5
6
7try {
// 可能发生异常的语句
} catch (Exception) {
// 异常处理
} finally {
// 一定会执行的代码
}
例:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public void divide(int a, int b) throws Exception {
int c;
if(0 == b) {
// 抛给 method 的调用者
throw new Exception("divided by 0");
}
c = a/b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
int result = divide(1,0);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("error, cause: " + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println(result);
}
在 try - catch - finally 语句块中:
- 有 try 子句必有 catch 子句或者 finally 子句;
- finally 子句中的内容一定会被执行,除非在 try 或者 catch 子句中含有 JVM 终止的语句(
System.exit(0);); - 若 try 部分中有返回值(
return),则将会先将该 return 语句挂起,先执行 finally 部分;- finally 子句在 try 或 catch 子句中的 return 语句执行之后(如 return 紧接一个运算或方法调用),return 返回之前(方法出栈);
- 如果 finally 中没有 return,则:如在 finally 块中修改原来 try 要返回的变量值,则不会影响该变量值;
- 如果 finally 子句和 try 或 catch 语句中都有 return 语句,真正返回的是 finally 中的 return 语句。
另:可自定义异常 —— 继承 Exception / RuntimeException 类